Kaggle Notebook Tips
You might have been working on Jupyter notebook, VS Code, Google Colab. Kaggle notebook is yet another one if you plan to join the competition. You don’t need to learn specifically for Kaggle notebook, because most skills you used in others still apply. But Kaggle notebook geared more toward Kaggle competition. So I try to leverage those features which are unique to Kaggle notebook to maximize the benefits of what Kaggle notebook has to offer.
I try to explore the follow common scenario:
- If I need to repeatedly use the same environment, how can I use the one I created before and not need to retype commands again?
You can save the notebook with the installation command as utility script (File>set as utility script). Then in your main notebook, you can import the utility script.
-
I would like to install RAPIDS and use it speed up with data manipulation and machine learning
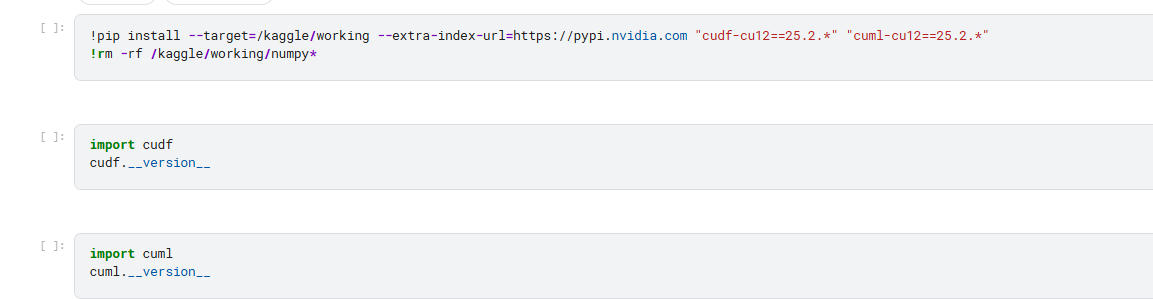
-
In the main notebook, you input it as utility script
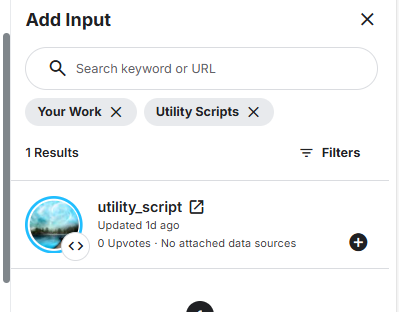
-
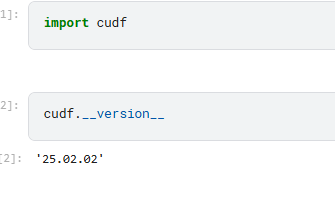
You can then use it in the new notebook. What I observe is the new notebook will install the package again. But you don’t have to remember the command.
in this case, I import package and check the version.
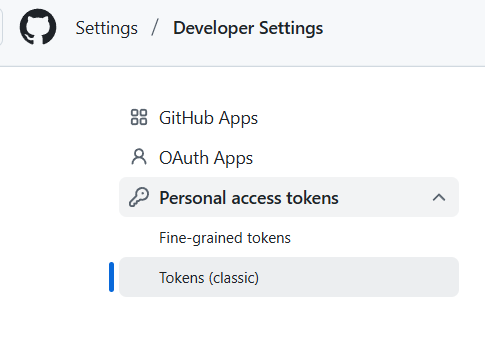
- What if you refactor your function and save it in a Github repo as python file, how are you able to load it?
- go to your repo and click the account icon, you can find the setting and developer setting.
you can set up a access token.
- go to your repo and click the account icon, you can find the setting and developer setting.
you can set up a access token.
-
in your kaggle notebook you can use the token value to set up a secret in key value format. in my case, I call it github.
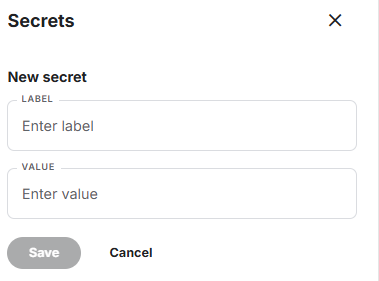
-
Kagge provide a way to clone github.
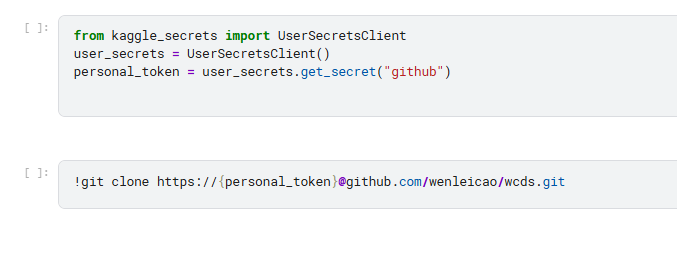
-
I actually also put this in utility script. in the main notebook, I can import the package and check one of function inside.
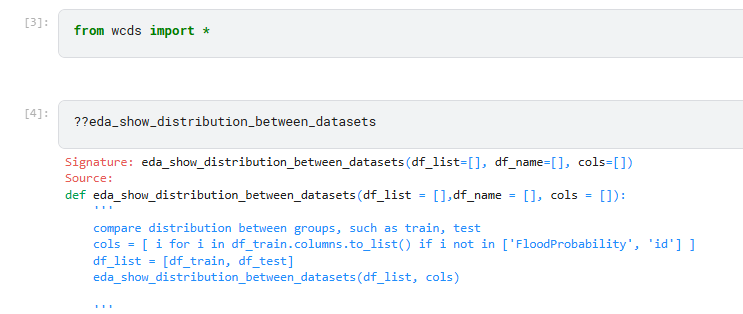
- You create a dataset in one notebook and would like it to be used in others.
- output your dataset as a file, in this case, I ouput the iris dataframe as a csv file.
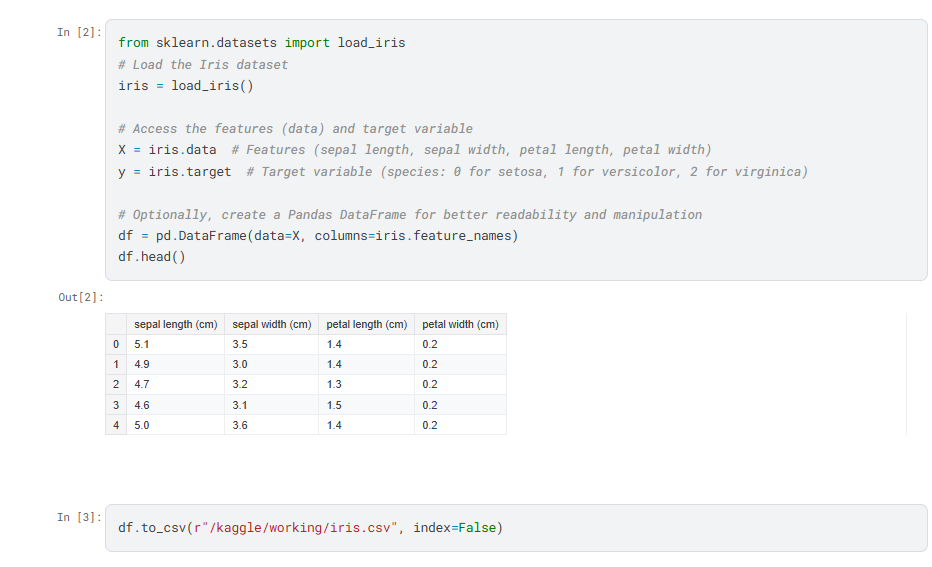
- output your dataset as a file, in this case, I ouput the iris dataframe as a csv file.
-
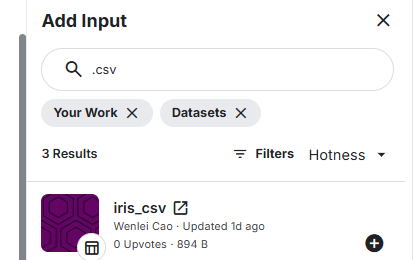
you then need to upload the csv file as dataset (not sure if upload is right word here, but it will convert csv to dataset)
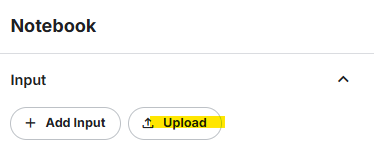
-
In you main notebook, input this dataset. You are all set.
I am sure there are other useful snippets. I will add more if I come across.
thanks
Wenlei
