Spark RDD join operation with step by step example
Compared with Hadoop, Spark is a newer generation infrastructure for big data. It stores data in Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDD) format in memory, processing data in parallel. RDD can be used to process structural data directly as well. It is hard to find a practical tutorial online to show how join and aggregation works in spark. I did some research. For presentation purpose, I just use a small dataset, but you can use much larger one.
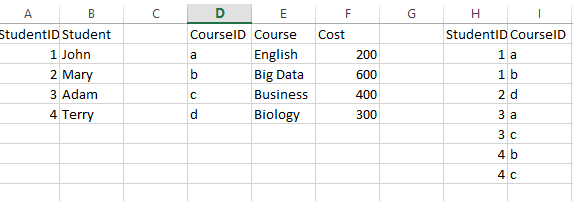
Here is a common many to many relation issue in RDBMS world.
Notice each student could have multiple courses, and vice versa. Now question is “we want to know each person how much they spend on the course” In SQL, you would write
select s.student, sum(c.cost)
from student s
inner join studentcourse sc on s.StudentID =sc.StudentID
inner join course c on sc.CourseID =c.CourseID
group by s.student
How this will happen when you use RDD? Let us import student, course, studentcourse data into RDD. If you want to repeat, I have files download link below, make sure you change the file path to your file location
val student = sc.textFile(“file:///home/mqp/Documents/test_data/Student.txt”)
val course = sc.textFile(“file:///home/mqp/Documents/test_data/Course.txt”)
val studentcourse = sc.textFile(“file:///home/mqp/Documents/test_data/StudentCourse.txt”)
Since imported data a line of string, we need to tokenize it to break it into studentID and name… Here I convert string to int for ID and cost. Notice string array start from 0, deliminator is tab
val student1 = student.map(rec => (rec.split(“\t”)(0).toInt, rec.split(“\t”)(1)))
val course1 = course.map(rec => (rec.split(“\t”)(0), rec.split(“\t”)(1),rec.split(“\t”)(2).toInt))
val studentcourse1 = studentcourse.map(rec => (rec.split(“\t”)(0).toInt, rec.split(“\t”)(1)))
Let us make sure RDDs contain what it is supposed to
student1.collect().foreach(println)
course1.collect().foreach(println)
studentcourse1.collect().foreach(println)
Since we found data is correct, we proceed to first join student with studentcourse
val join1 =student1.join(studentcourse1)
join1.collect().foreach(println)
RDD join can only be done in the form of key value pair. Once it is joined, the value of both RDD are nested. Becasue we need courseID to further join with course RDD, we need name for final result. We need to remap the postion of join result. Notice the syntax how to get the nested value. The second element of the result is rec._2.
val join1Remap = join1.map (rec =>(rec._2._2, rec._2._1))
join1Remap.collect().foreach(println)
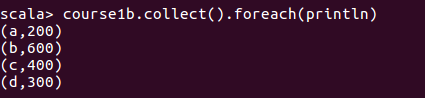
On the course RDD side, we only need course RDD CourseID and cost field. Therefore, we map that
val course1b = course1.map (rec=>(rec._1, rec._3))
course1b.collect().foreach(println)
Now we can join join1remap and course1b RDD. Both of them has courseID as key
val join2 = join1Remap.join(course1b)
join2.collect().foreach(println)
We only need student name and course cost
val join2b = join2.map (rec=>(rec._2._1, rec._2._2))
join2b.collect().foreach(println)
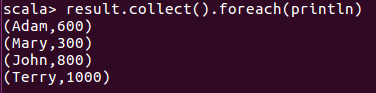
Aggreagation by reducebykey function
val result = join2b.reduceByKey ((acc, value) => acc+value)
result.collect().foreach(println)
You can see the result are summed correctly. There is a spark module call Spark sql which handles structrual data. You need to convert your RDD to dataframe to be able to use sql syntax. For compliated query, it is the way to go. If RDD format is ready for reduce job, it is faster to use RDD join directly.
Good luck.
Wenlei