Use Optuna to Tune Sklearn Pipeline Hyperparam
Pipeline makes data scientists’ life easier by combining different data transformation together. You just place a training dataset on one end, the other end is a model to be trained. By the time you want to predict, you just input the test data instead. Pipeline will process test data the exact same way as training dataset and help you get correct predictions.
Most people use Sklearn pipeline with GridSearchCV or RandomizedSearchCV for hyperparameter tuning. Those tools are good, but much like brute force to loop through all hyperparameter combinations. People are thinking if there are smarter ways to search for optimized hyperparameters. Optuna, a third party tool, has become popular lately by offering various search algorithms and pruning features. It also works with all major machine learning frameworks. I have seen many examples of Optuna working with tuning Xgboost, Catboost, model hyperparameters. But I don’t see Optuna being used for Sklearn pipeline hyperparam tuning. Imagining if you need to tune pipeline and model hyperparam separately, that would be awkward.
In this post, I try to see if I can use Optuna to tune Sklearn pipeline hyperparam as well as model hyperparam. I am going to present a working notebook. So, there are some extra cells which I used to test other ideas. But our focus here is to explore how to use Optuna for Sklearn pipeline hyperparam.
A Sklearn pipeline is composed of various transformers. Besides pre-made transformers, there are two types of custom transformers. One is the class based transformer, which is an instance of BaseEstimator. The other transformer is created by functiontransformer. The latter is a shortcut way, but only can be used for transformation that does not need to store the state, which is also called stateless transformation. For example, in order to impute the null value in a test dataset, you need to store medium (or whatever imputation strategy) value of training data so that both dataset are treated fairly. This is called stateful transformation.
This example notebook is about predicting Abalone’s age. Abalone is a sea creature by the way.
I have an “add feature” function which I use to add additional features to the dataset. Notice in this function, I have flags. If I select the flag, it will create the features. But I don’t know if these feature are useful. Therefore, I need to tune these hyperparam. I will use functiontransformer to convert this function to transformer to be used in pipeline.
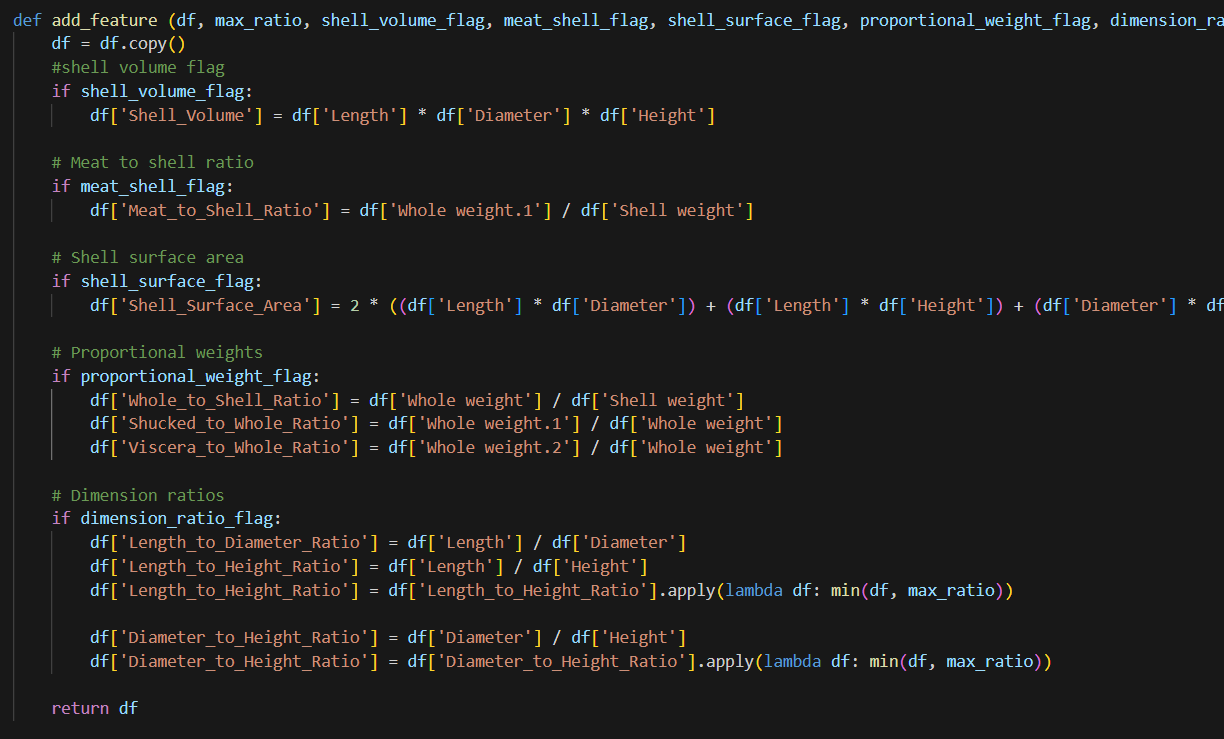
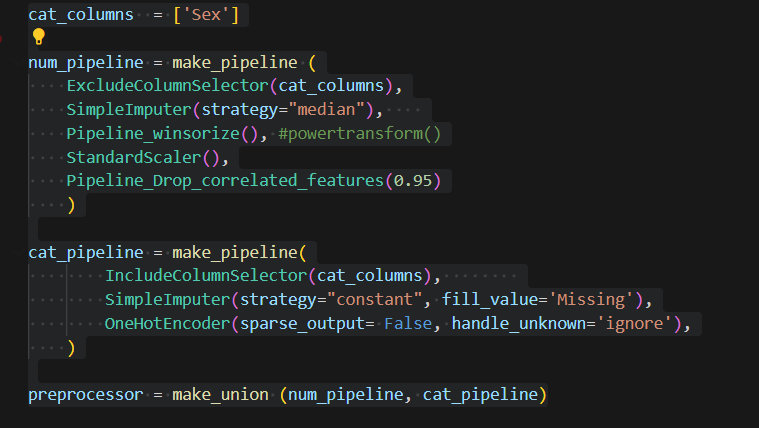
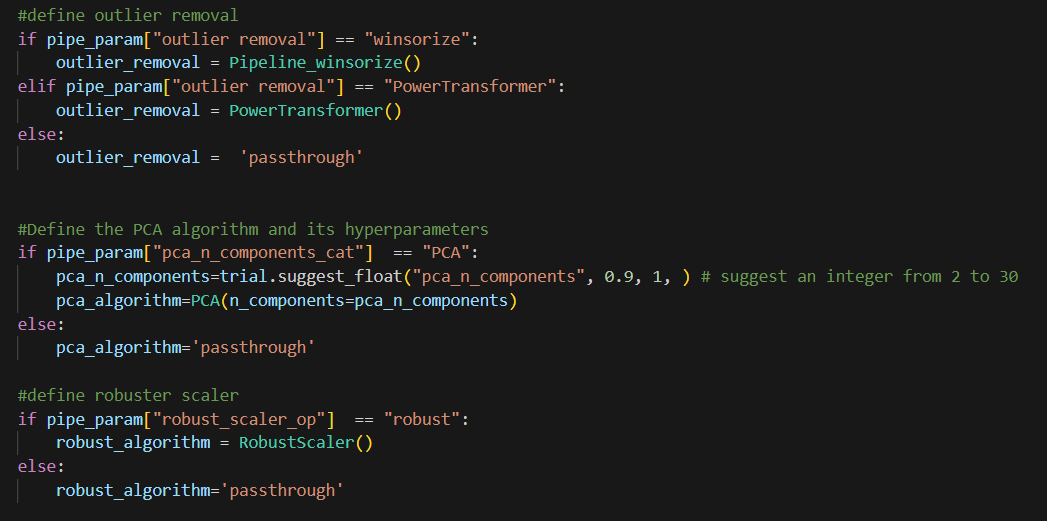
After I add these features, I need to handle numeric features and categorical features separately for some preprocess. In this dataset, there is only one categorical feature. I first choose columns, then imputation, winsorize is used to remove outliers (you can use powertransform too, scaler to scale all number in a certain range, I also include a custom transformer, which if two features are highly correlated , this transformer can drop one of them. There is a threshold need to tune.
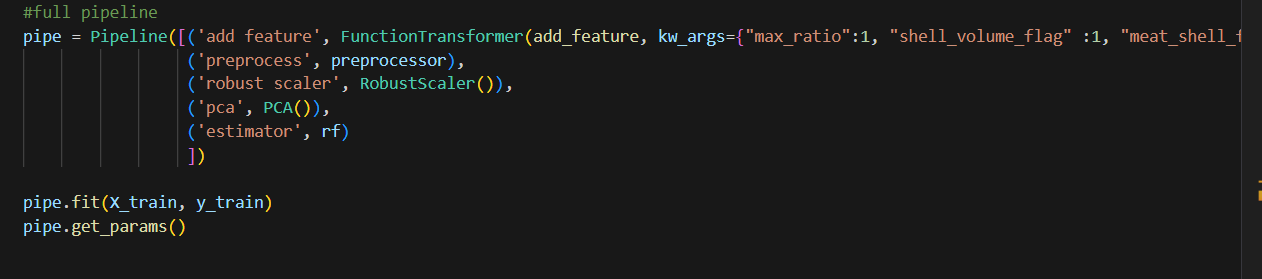
This is the full pipeline that I put different components together. Notice the special format when using functiontransformer. Also, I include RobustScaler before PCA since PCA is sensitive to value. I am not sure if RobustScaler and PCA will improve the model performance. We will tune to see. Here I use random forrest as a model placeholder.
This is the whole pipeline structure.
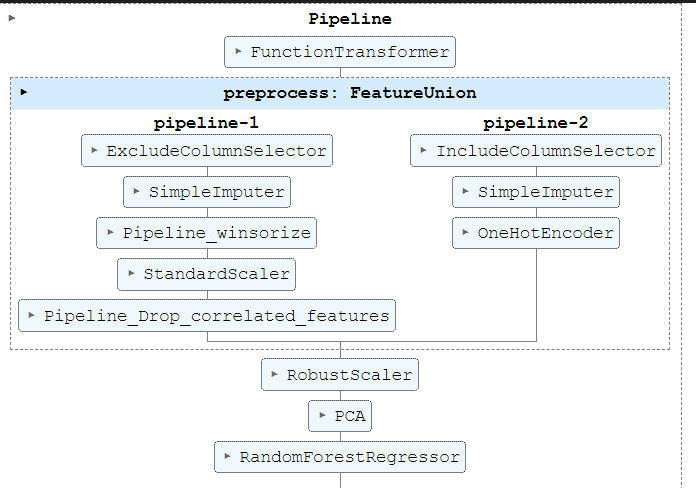
Usually here, you can place the pipe in GridSearchCV and tune the param. But our goal is to tune everything in Optuna. So we will need to make some modifications to our code.
In order to use Optuna for hyperparmeter tuning, we will need to create an objective function. First import necessary library. I am going to tune lightgbm model with pipeline.
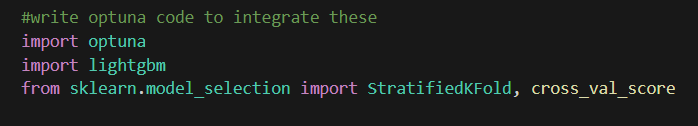
Optuna does not allow you to choose objects directly. So what we can do is use suggest_categoircal to choose a string, Then, use string variable to set the object later.
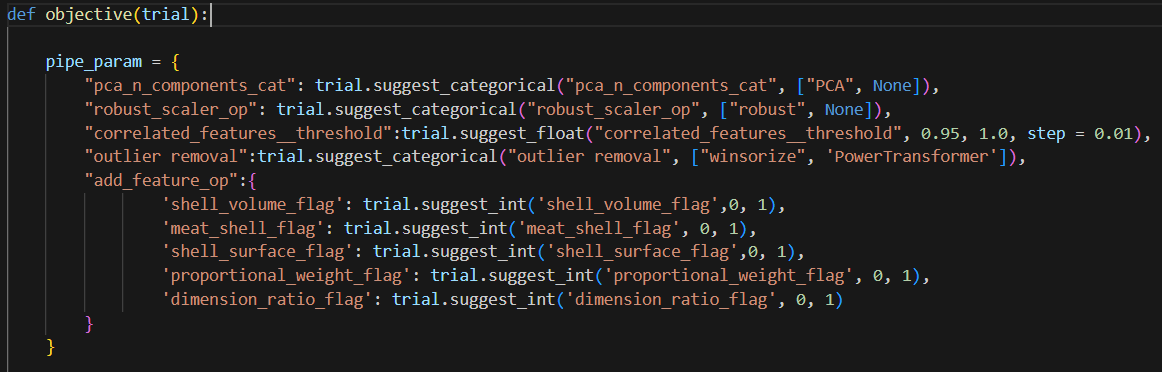
Now, once Optuna chose a string value, we can use the if clause here to define the object we need.
These variables will be used in the pipeline as follows, see yellow highlight area.
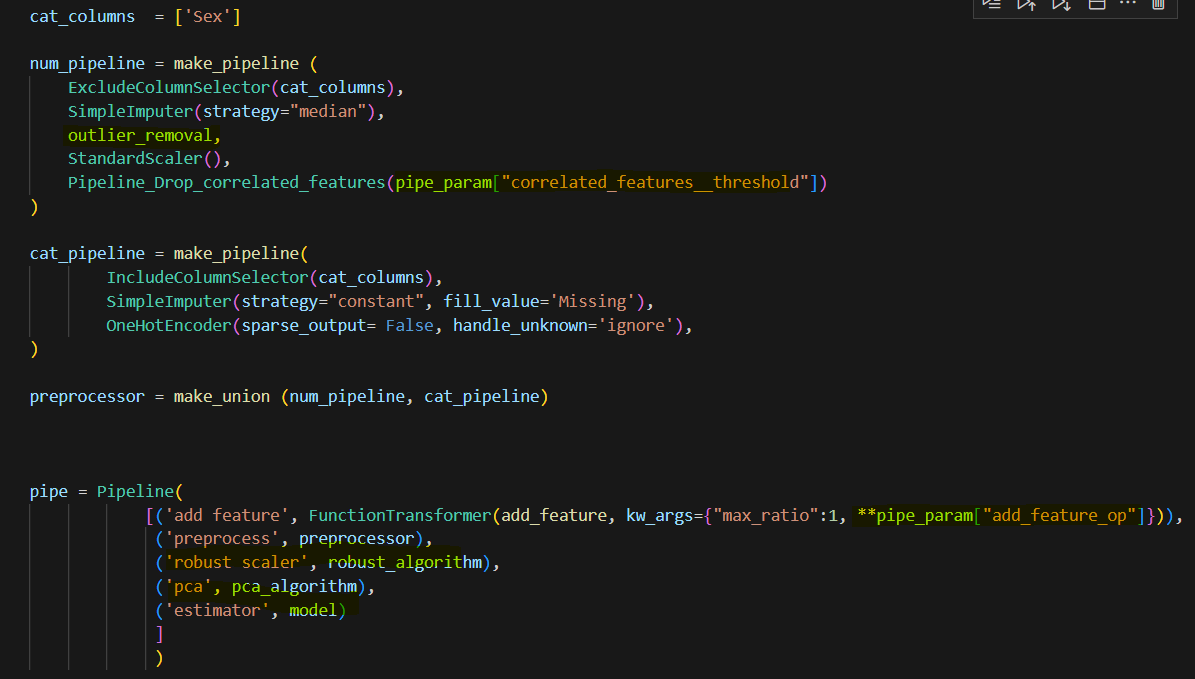
Also before the pipe step, I included lgbm hyperparams and created the model. This model will be used in the pipe above.
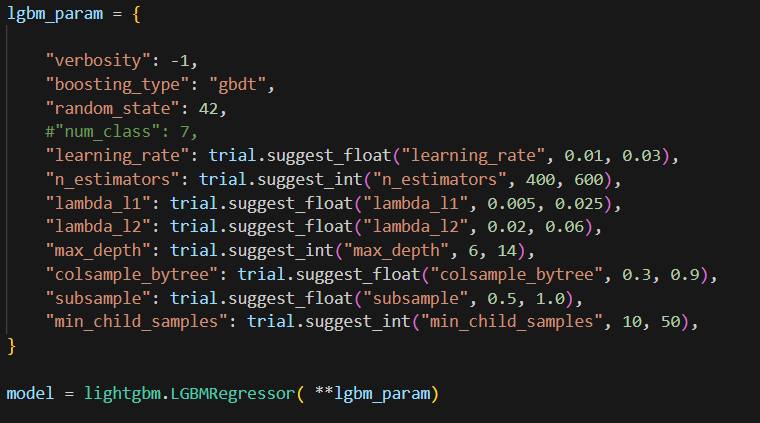
Finally, we use pipe in the cross_val_score. And this objective function is used to create a study. In this study, I ran 100 trials.
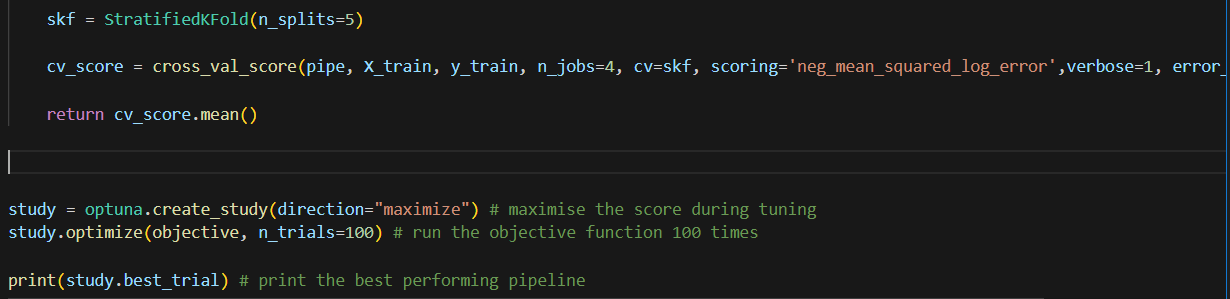
This is trial log.
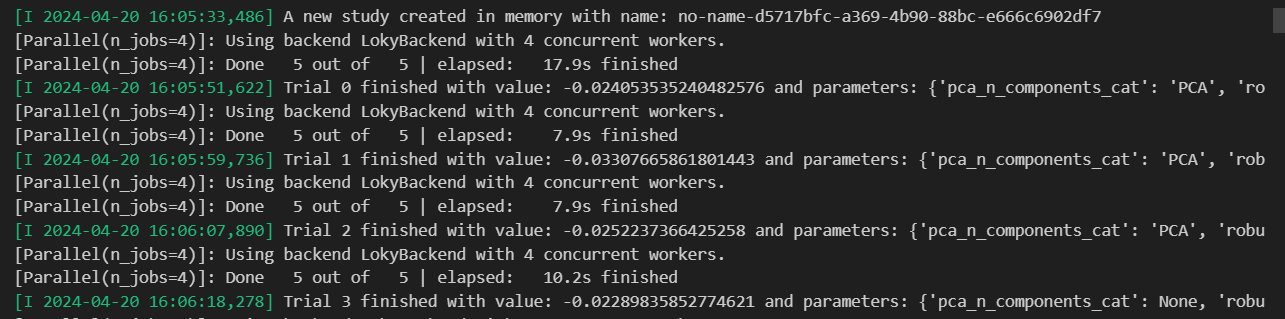
At the end, I can print the best param. Looks like it does not choose to use PCA, robustscaler. Outlier removal chose to use winsorize. Here due to the size of the window. It cannot show all params. But you will see the chosen param for lgbm in the notebook.

So it is possible to tune pipeline hyperparam with model hyperparam. We can do it in one go.
Hope you feel this is useful.
As usual, you can find notebook here.
thanks
Wenlei
